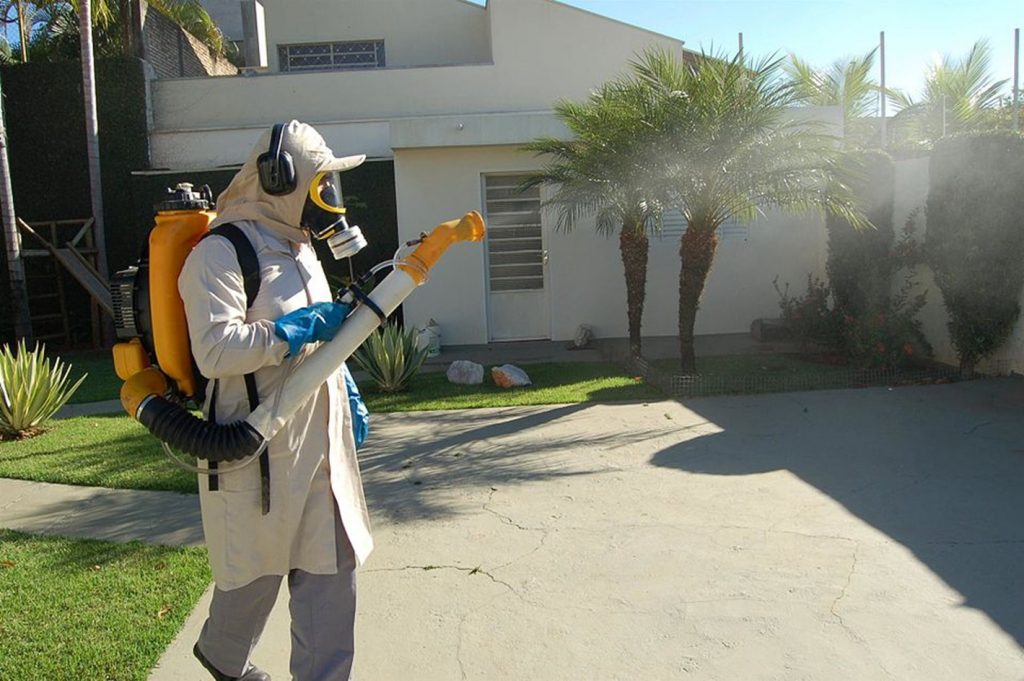
Figure 1. Municipal agent in Votuporanga, Brazil, fumigating a house. Source: Flickr
Artificial intelligence (AI) is not just reshaping daily life, it is revolutionizing how scientific research is being done and how it is applied for global public health. In the fight against dengue, AI plays a critical role in predicting outbreaks, mapping high-risk areas, and enhancing mosquito control strategies. Latin America is emerging as a leader in applying these innovations.
Table of Contents
Predictive Modeling for Outbreak Forecasting
A major challenge in dengue control is anticipating outbreaks. A 2022 study by Roster et al., published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, developed AI-based models to predict monthly dengue cases across Brazilian cities up to one month in advance.
Using data from 2007 to 2019, they tested several machine learning algorithms, including Random Forests, Gradient Boosting, Neural Networks, and Support Vector Regression, alongside weather variables like temperature, rainfall, and humidity.
They assessed their performance using Mean Absolute Error (MAE) between predicted and actual monthly dengue cases.
Their key finding was that random forests performed best overall, but localized models worked better for different regions, highlighting the need for city-specific AI solutions.
Machine Learning for Diagnosis and Intervention
In another study, Bohm et al. (BMC Public Health) used machine learning to develop effective strategies for control, diagnosis, and treatment of dengue cases in Rio de Janeiro and Minas Gerais from 2016–2019.
They tested several machine learning models, including Logistic Regression, Decision Trees, and Multilayer Perceptrons (MLP). The best-performing models used just 10 clinical variables (e.g., such as gender, fever, and headache) for accurate classification, and the decision tree and multilayer perception (MLP) model achieved the best result for its balance of accuracy and speed.
In the real world, these models can be integrated into mobile or desktop tools to help healthcare workers quickly screen patients and prevent disease progression
From Drones to Data: How AI Enhances Biological Dengue Control

Figure 2. Artificial intelligence. Source: Wikimedia Commons.
In the research by Beraldo et al., the authors conducted an extensive literature review to uncover key factors driving high dengue incidence in Brazil. Their findings highlight how artificial intelligence (AI) is now being integrated with biological control methods to enhance mosquito management. A data-driven approach can reduce reliance on chemical pesticides and provide a more effective, long-term solution for dengue prevention.
Utilization of AI can enhance biological control in multiple ways:
- Hotspot identification: AI pinpoints areas with high mosquito density, improving precision of mosquito releases and minimizing environmental impact.
- Ecological analysis: AI evaluates the effectiveness of natural predators in specific regions, allowing better local adaptation.
- AI-powered drones and computer vision: Used to rapidly detect breeding sites in hard-to-reach areas, enabling broader application of biolarvicides.
- Community education and engagement: Demographic data is used to design local awareness campaigns. Chatbots and virtual assistants offer real-time info, empowering communities to prevent dengue spread.
Modeling Mosquito Control with AI: Case Studies
Wolbachia-Based Modeling – Iftikhar et al. (2020)
Published in Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, this study presents a novel AI strategy for enhancing Wolbachia-based control of Aedes aegypti. Researchers used numerical simulations to model different mating scenarios, forecast population dynamics, and optimize dengue suppression strategies.
They developed mathematical frameworks supported by AI tools to estimate accurate parameters, enabling better planning of future experimental studies. This modeling approach can also extend to other diseases like Zika and Chikungunya.
Genetic Modification Modeling – da Silva et al. (2022)
In a paper published in Scientific Reports, da Silva et al. used AI to model the impact of genetically modified (GM) male mosquitoes on Aedes aegypti population dynamics.
Traditional methods like insecticides are losing effectiveness due to high mosquito reproduction rates. The study developed a simplified AI-backed model to simulate how varying the frequency and quantity of GM male releases influences population suppression.
Overall, their simulations show that successful suppression of Aedes aegypti depends on releasing GM males above a critical threshold in both quantity and frequency. The environment, such as habitat heterogeneity, also influences its effectiveness. This model provides a more accessible tool for planning and optimizing GM mosquito release strategies in ecological setting.
The results emphasized the need to exceed a critical release threshold, while accounting for environmental factors like habitat heterogeneity.
The Takeaway
These studies underscore the growing synergy between AI and biological control. Together, they offer smarter, more sustainable, and highly targeted strategies for fighting dengue and other vector-borne diseases. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into public health and ecological models could reshape the future of global disease prevention.
From disease forecasting to clinical support tools, AI enables faster, more targeted responses to dengue. As more data becomes available, these systems will become even smarter, able to empower both public health officials and frontline clinicians.